In a certain range increasing the thermal conductivity of ceramic materials by specific methods will improve its ability of heat conduction heat convection and heat radiation so as to further expand its application field.
Low thermal conductivity ceramic materials.
Zirconium dioxide zro 2 sometimes known as zirconia not to be confused with zircon is a white crystalline oxide of zirconium its most naturally occurring form with a monoclinic crystalline structure is the mineral baddeleyite a dopant stabilized cubic structured zirconia cubic zirconia is synthesized in various colours for use as a gemstone and a diamond simulant.
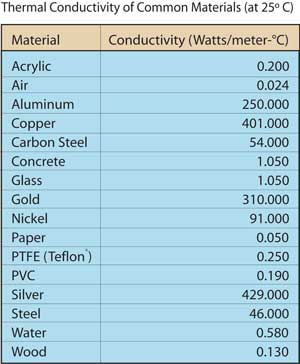
Looking at the values quoted in various handbooks papers and data sheets two things are observed.
Learn about product material thermal conductivity.
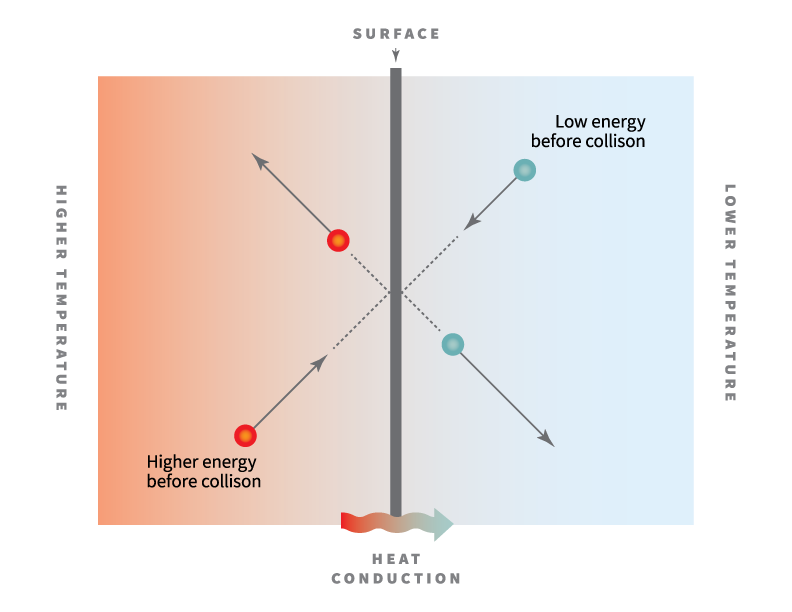
The property that measures how well heat is transmitted through a material is called thermal conductivity.
Ceramics with high or low thermal conductivity can be selected from our materials list.
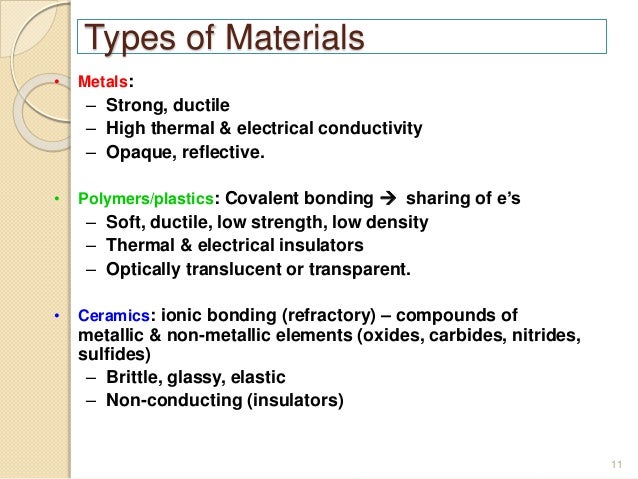
Thermal conductivity is a material property that describes ability to conduct heat thermal conductivity can be defined as the quantity of heat transmitted through a unit thickness of a material in a direction normal to a surface of unit area due to a unit temperature gradient under steady state conditions.
The compressive strength could be improved significantly by increasing the sintering temperature.
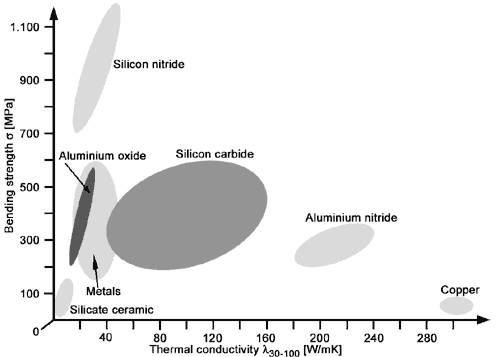
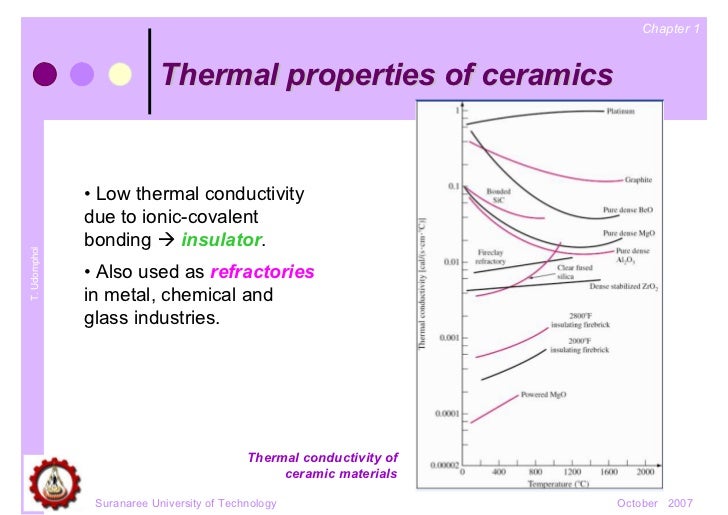
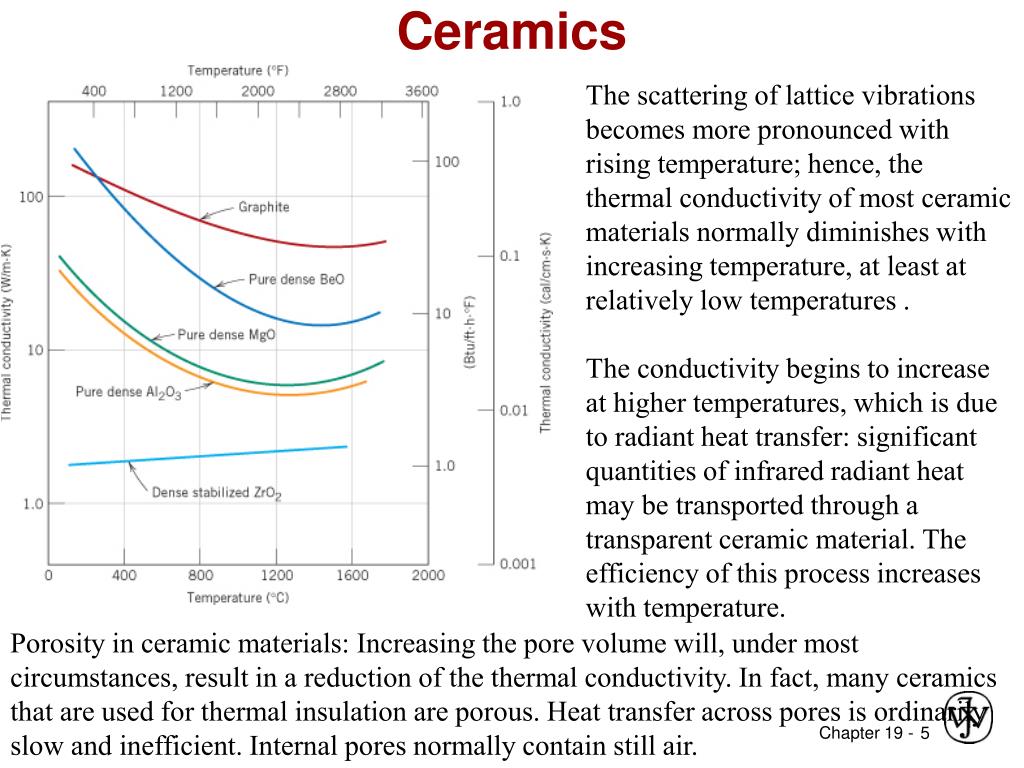
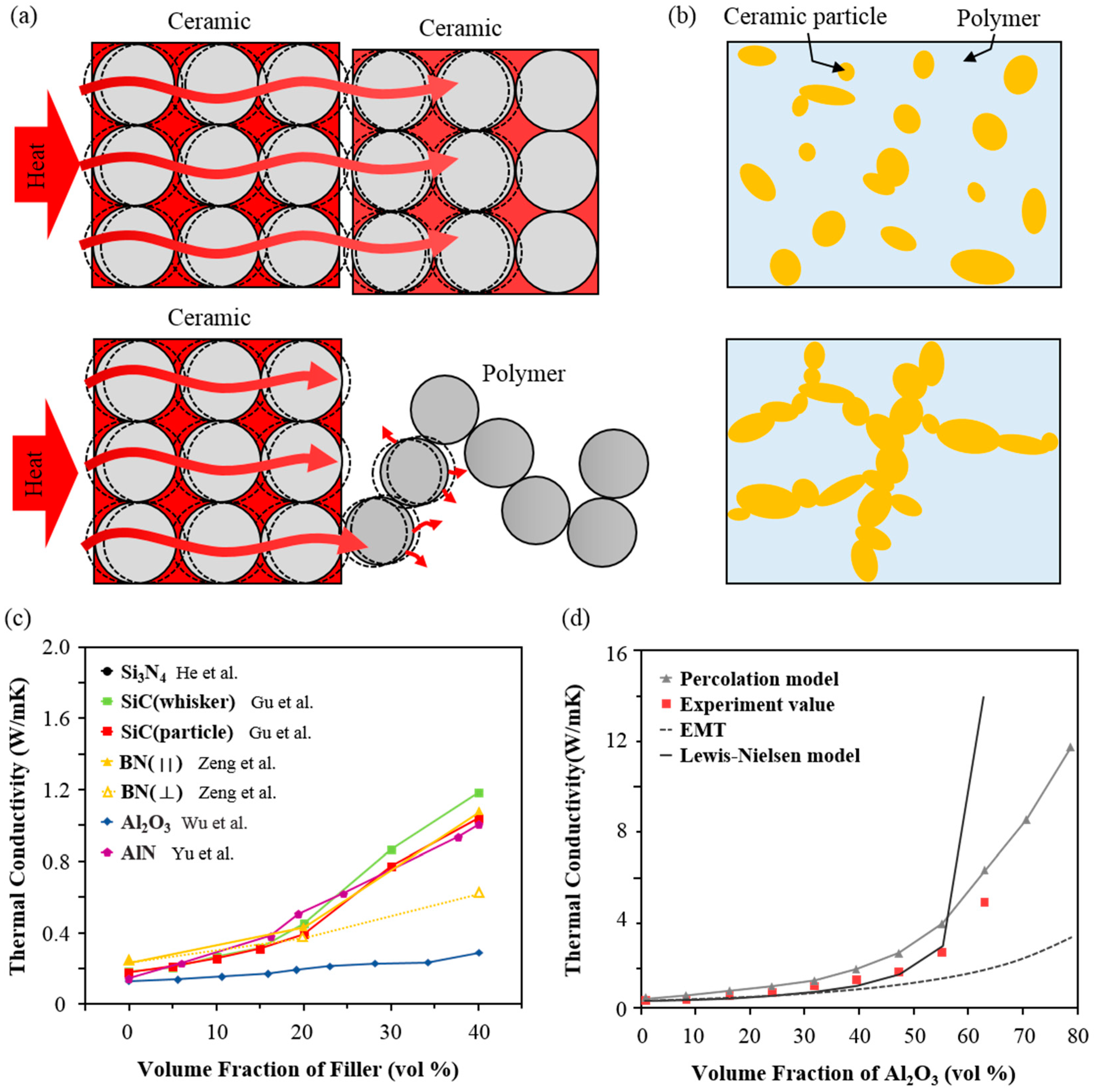
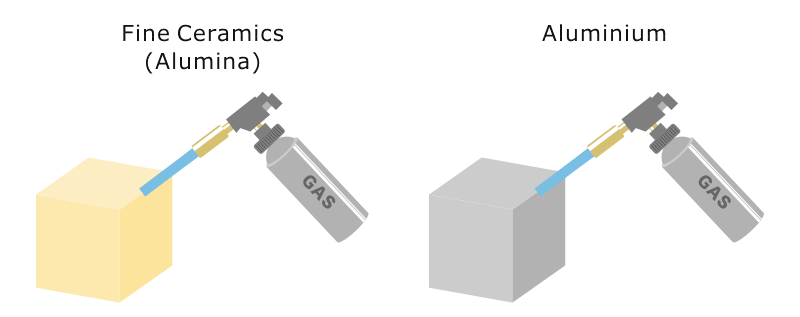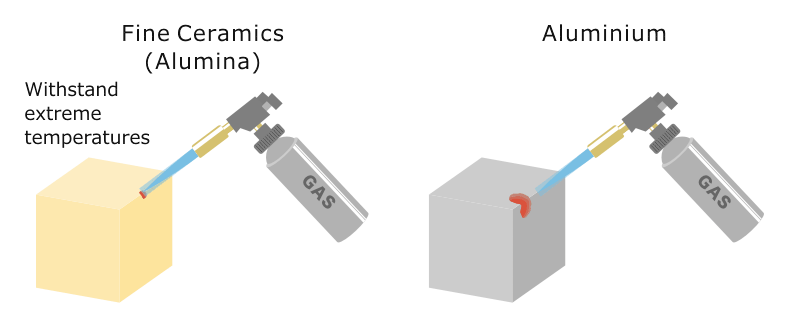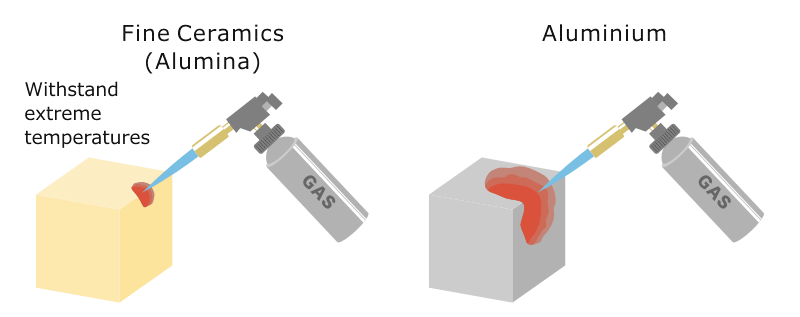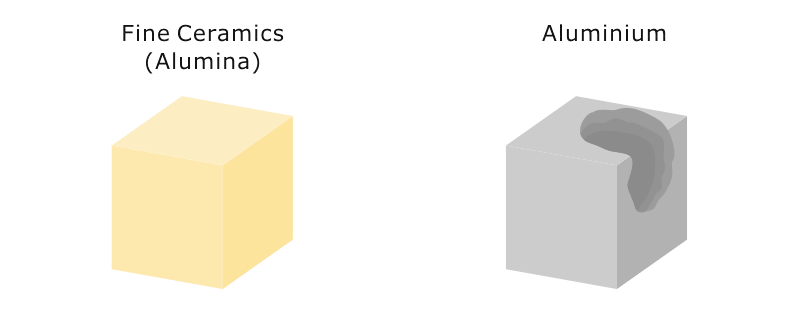
The thermal conductivity of ceramic materials plays an important role in its application.
Twelve commercial ceramic materials were selected for this irradiation study and are listed in table 1 along with their room temperature physical properties.
Of importance is that for some of the materials sic and al 2 o 3 different ceramic grades are used to obtain different non irradiated thermal conductivities for nominally equivalent base materials.
Among fine ceramics also known as advanced ceramics some materials possess high levels of conductivity and transfer heat well while others possess low levels of conductivity and transfer less heat.
A novel high entropy carbide ceramic hf 0 2 zr 0 2 ta 0 2 nb 0 2 ti 0 2 c with a single phase rock salt structure was synthesized by spark plasma sintering x ray diffraction confirmed the formation of a single phase rock salt structure at 26 1140 c in argon atmosphere in which the 5 metal elements may share a cation position while the c element occupies the anion position.
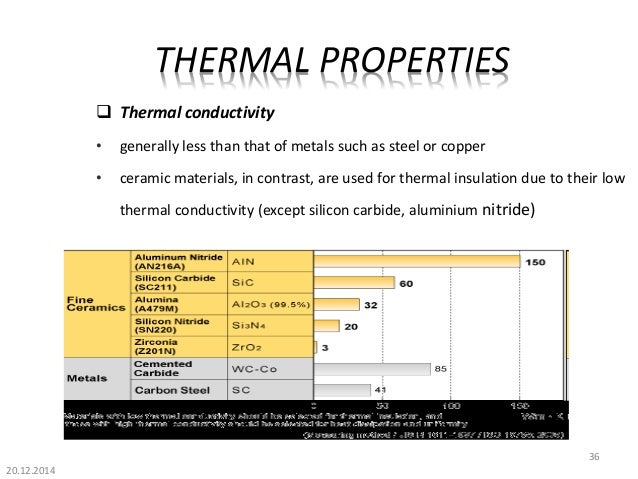
Silicon carbide sc1000 200.
Zirconia ceramic foams with porosity of 97 9 has low thermal conductivity of 0 027 0 004 w m k 1 which could be used as thermal insulation and refractory material.
These thermal greases have low electrical conductivity and their volume resistivities are 1 5 10 15 1 8 10 11 and 9 9 10 9 ω cm for 860 8616 and 8617 respectively.
Decreasing solid loading leads to the porosity of ceramic foams.